What Is Asset Disposal in IT Asset Management?
Discover key steps and methods for IT asset disposal, including data sanitization and compliance with regulations.
What is Asset Disposal in ITAM?
Asset disposal in IT Asset Management (ITAM) is the process of responsibly removing IT assets that are no longer in use. This could be anything from old computers and servers to outdated software and mobile devices.
When IT equipment is no longer needed because it is too old, broken, or replaced with newer technology, it must be disposed of properly. This means not just getting rid of the hardware but also ensuring that any sensitive data on it is securely erased to prevent unauthorized access.
In addition to data security, proper asset disposal also means following legal and environmental guidelines to avoid contributing to e-waste. Sometimes, this can involve recycling, reselling, or donating equipment that is still functional.
In short, asset disposal is about managing outdated equipment in a way that keeps your organization secure, compliant, and environmentally responsible.
Types of Asset Disposal
There are several ways to dispose of IT assets, and the right method depends on the condition of the asset, your organization’s needs, and environmental considerations. Here are the most common types of asset disposal:
- Recycling: Recycling involves breaking down old IT equipment into its raw materials - such as metals, plastics, and glass - which can then be reused in new products. This is an environmentally responsible way to dispose of non-functional or obsolete devices that can’t be reused.
- Reselling or Donating: If an asset is still functional but no longer needed, it can be resold or donated. Reselling allows organizations to recover some of the asset’s value, while donating functional equipment helps extend its life and supports those in need, such as schools or charities.
- Trade-In: Some technology vendors offer trade-in programs where you can exchange old assets for credit towards new equipment. This can be a convenient option for upgrading technology without the hassle of managing disposal on your own.
- Landfill Disposal (Last Resort): As a last resort, if the asset is beyond repair and cannot be recycled, it may end up in a landfill. However, this method should be avoided as it contributes to e-waste and environmental pollution.
Each of these disposal methods offers different benefits, so choosing the right one depends on your asset’s condition and your organization’s goals for security, compliance, and sustainability.
Importance of Asset Disposal in ITAM
Proper asset disposal is a vital part of IT Asset Management (ITAM). It goes beyond just clearing out old equipment. It is about protecting your organization from risks, meeting legal requirements, and supporting environmental sustainability.
- Protecting Sensitive Data: When you dispose of IT assets, it’s crucial to ensure that all sensitive data is securely erased. Simply deleting files is not enough. Proper data destruction prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information and reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Meeting Legal and Industry Requirements: Different industries have regulations that require secure disposal of IT equipment. Laws like GDPR and HIPAA require businesses to follow specific disposal procedures to protect personal and confidential data. Failing to do so can lead to fines or legal issues.
- Reducing Environmental Impact: IT equipment often contains materials that can harm the environment, such as metals or chemicals. By recycling or reusing equipment, you help reduce e-waste and support sustainability efforts, making sure harmful materials don’t end up in landfills.
- Maximizing Asset Value: Even old IT equipment can still have value. Whether it’s reselling, recycling, or donating, your organization can recover some of the asset’s original cost. This not only helps others but also reduces the financial impact of purchasing new equipment.
In short, asset disposal is an essential process that protects your organization’s data, ensures compliance with regulations, reduces environmental harm, and can even provide financial benefits.
Steps Involved in IT Asset Disposal
Disposing of IT assets the right way is crucial to keeping your organization safe, compliant, and environmentally responsible. Here’s a simple guide to the main steps involved in the process:
1. Inventory Check
The first step is figuring out which assets need to be disposed of. A good inventory check ensures you’re only getting rid of outdated or broken equipment, not something that’s still useful.
How to do it:
- Regularly review your inventory and check which items are old, broken, or no longer needed.
- Keep track of the asset details, like serial numbers and warranty info.
Why it matters:
By checking your inventory regularly, you make sure that no valuable equipment is accidentally thrown out. It also keeps your records up to date for audits or compliance checks.
2. Data Sanitization
Before you dispose of any asset, it’s important to make sure all sensitive information is wiped out. Simply deleting files doesn’t always work; data can still be recovered, so you need to securely erase it.
How to do it:
- Use data wiping software to permanently erase the data on your device.
- For hard drives and other storage devices, consider physical destruction like shredding or crushing.
- If you’re unsure, use a professional service to securely destroy the data.
Why it matters:
Data sanitization is essential to prevent data leaks or breaches. It ensures no sensitive information is left behind, helping you avoid security risks and stay compliant with data protection laws.
3. Disposal Method Selection
Once the data is erased, you need to decide the best way to dispose of the asset based on its condition and your goals, whether that’s recycling, reselling, or donating.
How to do it:
- Recycling: If the asset doesn’t work anymore, send it to a certified e-waste recycling facility.
- Reselling: If the asset is still in good shape, sell it to recover some of its value.
- Donating: If the equipment is functional but not needed, donate it to a school, nonprofit, or charity.
- Trade-In: Some tech vendors will take your old equipment in exchange for credit towards new products.
Why it matters:
Choosing the right disposal method helps reduce waste, get value back from old assets, and contribute to sustainability efforts. It’s also an eco-friendly option, as it keeps working equipment out of landfills.
4. Vendor Selection (if applicable)
If you’re using a vendor to handle the disposal, choosing a reliable one is key to ensuring the process is secure and compliant.
How to do it:
- Look for vendors with certifications like R2 or ISO 14001, which show they follow best practices.
- Ask for proof that they use secure data destruction methods and environmentally-friendly practices.
- Make sure they provide documentation for each disposal, like certificates of data destruction.
Why it matters:
A trustworthy vendor will ensure that your assets are disposed of safely and responsibly. They will handle your assets in a way that protects your data and supports your environmental goals.
5. Documentation
Keeping records of the disposal process is important for compliance and future audits. Proper documentation shows that you followed the right procedures.
How to do it:
- Keep records of the asset details (like serial numbers) and how they were disposed of.
- Store certificates of data destruction and receipts from reselling or donations.
- Keep these documents safe for future reference.
Why it matters:
Documenting the disposal process ensures that you meet legal requirements and have a clear record of how assets were handled. It also helps you stay compliant with industry regulations.
6. Environmental Compliance
Properly disposing of IT assets also means following environmental rules to reduce e-waste and promote sustainability.
How to do it:
- Work with vendors who are certified to handle e-waste, like those following WEEE or RoHS standards.
- Ensure harmful materials (like mercury or lead) are disposed of correctly.
- Encourage recycling and reuse to support the circular economy.
Why it matters:
By complying with environmental regulations, your organization reduces its impact on the planet and helps avoid fines. It also supports sustainability efforts and reduces the amount of e-waste sent to landfills.
Following these steps ensures your IT asset disposal is done safely, legally, and with consideration for the environment. Each step helps protect sensitive data, stay compliant with regulations, and reduce your organization’s environmental footprint.
Signs You Need to Dispose of IT Assets
Knowing when to retire an IT asset is an important part of keeping your technology environment efficient, secure, and cost-effective. Holding on to devices for too long can slow down your team, increase security risks, and lead to higher maintenance costs. To help you make timely decisions, here are the most common signs that an asset is ready to be disposed of:
- Declining performance: The device becomes slow, freezes often, or struggles with basic tasks.
- No warranty or vendor support: The asset no longer receives updates, patches, or repair options.
- Frequent repairs: Maintenance costs keep increasing, or the device breaks down repeatedly.
- Outdated or incompatible technology: It cannot run modern software, connect to new systems, or meet current work requirements.
- Security concerns: The device can’t support the latest security updates, making it more vulnerable to threats.
- High energy consumption: Older equipment uses more power and adds to operating costs.
- Not in use anymore: The asset sits unused due to team changes, upgrades, or workflow adjustments.
Together, these signs help you decide when an asset is no longer worth keeping. Recognizing them early allows your organization to plan ahead, reduce risks, and maintain a healthier IT environment.
How to Choose the Right Asset Disposal Vendor
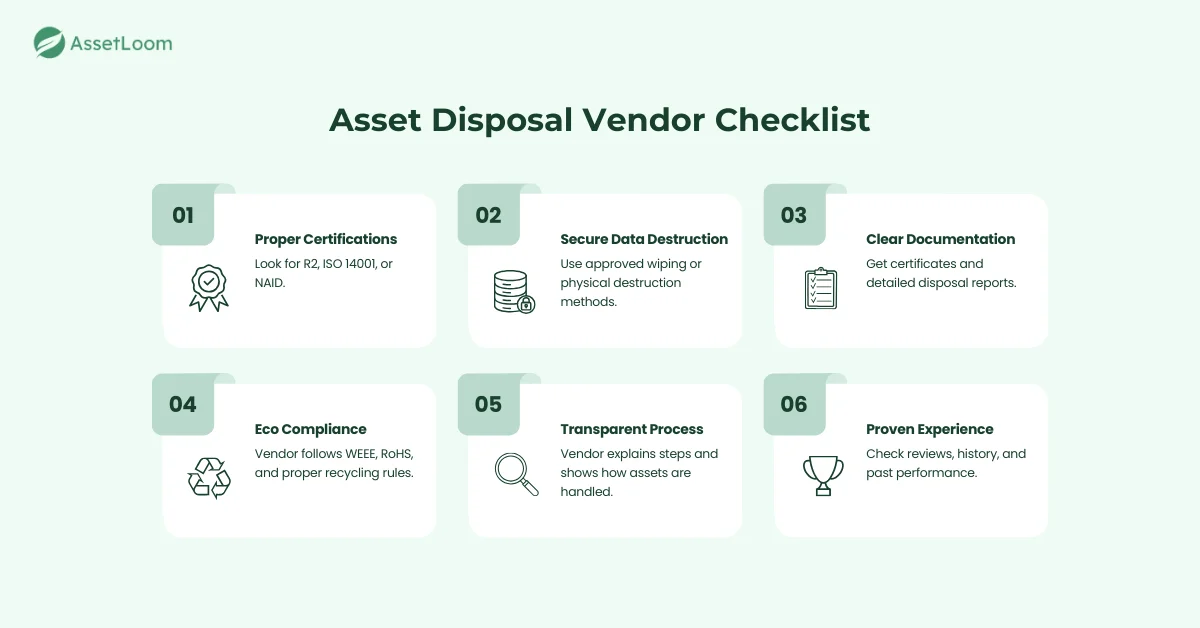
If you decide to work with a vendor for IT asset disposal, choosing the right partner is essential. A reliable vendor helps you handle data securely, follow environmental rules, and avoid unnecessary risks. Here’s what to look for when evaluating disposal vendors:
- Proper certifications: Choose a vendor that meets recognized standards such as R2, ISO 14001, or NAID. These certifications show that the company follows safe and responsible disposal practices.
- Secure data destruction methods: Make sure the vendor uses approved data wiping or physical destruction processes. Ask how they sanitize devices and whether they provide detailed reports.
- Clear documentation: A trustworthy vendor will provide certificates of data destruction, recycling reports, and any required compliance documents. This helps you maintain a complete audit trail.
- Environmental responsibility: Look for vendors that follow e-waste regulations like WEEE or RoHS, and that recycle materials responsibly. The right vendor should help you reduce environmental impact, not add to it.
- Transparent process: A good vendor explains each step of their disposal workflow and answers questions clearly. They should be open about how they handle devices from start to finish.
- Proven experience: Check their track record, client reviews, or case studies. Vendors with solid experience are more likely to handle your assets correctly and avoid common issues.
Choosing the right vendor gives you confidence that your assets are managed safely and responsibly. It also protects your organization from data leaks, compliance issues, and environmental risks.
Read also: 7 Vendor Management Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Glossary of Related Terms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What happens to the usable parts of an old IT asset after disposal?
If the asset is recycled, components like metal, plastic, memory modules, or screens may be recovered and reused. This helps reduce waste and supports the circular economy.
Can software licenses be reused after disposing of a device?
It depends on the type of license. Some licenses are transferable, while others are tied to the original hardware. Check the vendor’s licensing terms before disposal.
Should I dispose of all old devices at once or phase them out?
Many organizations remove devices in stages to reduce disruption, manage costs, and ensure smoother transitions to newer equipment.
How early should disposal planning begin in the asset lifecycle?
Planning should ideally begin at purchase. Tracking purchase dates, warranties, and usage helps you decide the right time for disposal later.
Do I need to reset devices before handing them to a disposal vendor?
A factory reset is helpful, but it’s not enough. Vendors will handle full data destruction, but clearing personal or account info first adds extra safety.
What if I am unsure whether an asset should be repaired or disposed of?
Compare repair costs with the asset’s remaining value. If repairs keep adding up or cost more than the device is worth, disposal is usually the better option.
Are there risks in storing old assets instead of disposing of them?
Yes. Storing unused devices can expose your organization to data risks, unnecessary storage costs, and physical degradation of equipment over time.