What is Asset Inventory Management? A Complete Overview
Master asset inventory management with our guide. Learn the benefits, best practices, and implementation strategies to optimize your assets.
Have you ever struggled to find important equipment when you need it most? Or spent extra money buying assets you already own? These problems are common when businesses don’t have an effective asset inventory system.
Every item in your business — from tech tools to office supplies — plays a vital role in daily operations. That’s why keeping your inventory accurate and organized isn’t just helpful; it’s essential.
In this article, we’ll cover the basics of asset inventory management, its main benefits, and how it differs from other management practices.
What is asset inventory management?
Asset inventory management is the process of systematically recording, tracking, and organizing both physical and digital assets within an organization. It helps businesses ensure they know exactly what assets they own, where they are located, and their condition at any given time.
This process involves more than just keeping a list of items. It’s about making sure every asset, whether it’s a computer, vehicle, or office equipment, is properly managed throughout its lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
Key aspects of asset inventory management include:
- Identification: Assigning a unique identifier (like an ID number or barcode) to each asset, which allows for quick and easy reference.
- Tracking: Continuously monitoring the location, usage, and movement of assets using software, RFID tags, or GPS systems.
- Recording: Keeping a comprehensive and up-to-date database that includes asset details such as purchase date, cost, maintenance history, warranty information, and depreciation values.
- Auditing: Performing regular physical checks and audits to ensure the asset database is accurate and resolving any discrepancies between records and actual assets.
A well-managed asset inventory system reduces errors and inefficiencies. It also improves financial planning and supports regulatory compliance. Tracking assets helps prevent risks like theft or damage. With clear visibility, organizations can make smarter decisions about usage, maintenance, and replacements. This leads to higher productivity and lower costs.
Types of asset inventory
Not all assets are the same, and understanding the categories can help tailor the right management strategies. Commonly, assets can be grouped into four main types.

1. Physical assets
Physical assets are tangible items such as furniture, vehicles, tools, and manufacturing equipment. These are often tagged or labeled using barcodes or RFID tags to facilitate easy scanning and tracking.
2. Digital assets
Digital or intangible assets include software licenses, cloud-based systems, digital media, and data repositories. Their tracking involves license management, version control, and secured access, making them more complex to manage than physical assets.
3. Intellectual property or Intangible assets
Though less visible, patents, trademarks, proprietary processes, and brand value all qualify as intellectual property. Therefore, managing these assets requires careful attention to legal documentation, renewal dates, and potential infringements.
4. Hybrid assets
Some assets integrate physical and digital components. For instance, IoT-enabled machinery and smart devices collect data continuously, combining physical presence with an online component. Managing these assets effectively requires tools that capture both physical and digital information.
Differences between asset management and inventory management
While asset management and inventory management are often mentioned in similar contexts, they serve distinct purposes within an organization. Understanding the differences between these two disciplines is crucial for implementing effective strategies that address specific business needs.
1. Their similarities
Both asset management and inventory management rely on accurate data tracking to function effectively. This means maintaining detailed records to monitor the status, location, and movement of items within the organization.
Key similarities include:
- Use of Technology: Both practices commonly rely on tools like barcodes, QR codes, RFID tags, and centralized databases to enable real-time tracking and easy access to information.
- Focus on Efficiency: Both aim to improve operational efficiency and control costs. By managing assets and inventory well, businesses can reduce waste, prevent losses, and maximize resource utilization.
2. Their differences
Asset Management
Asset management involves overseeing the entire lifecycle of an organization’s assets. This includes acquisition, maintenance, utilization, and disposal. The main goal is to maximize the value and performance of assets over time while aligning their use with the organization’s strategic objectives.
This approach covers:
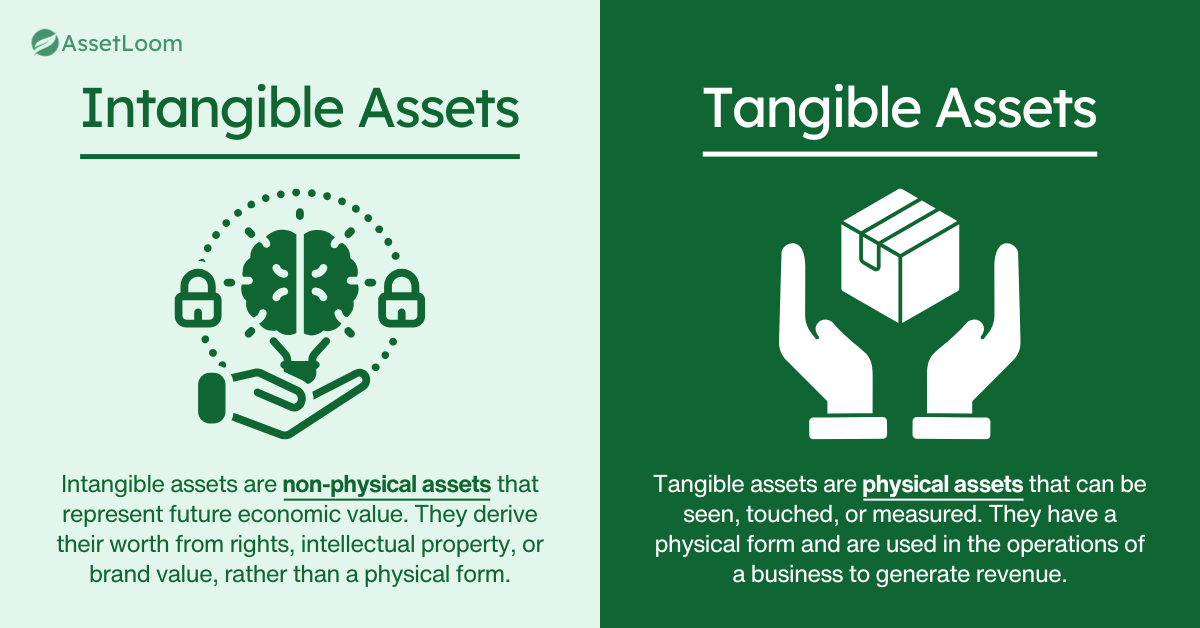
- Tangible assets: Machinery, vehicles, and physical equipment.
- Intangible assets: Software licenses, intellectual property, and other digital assets.
Effective asset management also requires skills in financial analysis, risk assessment, and strategic planning to ensure optimal asset performance and a strong return on investment (ROI).
Inventory Management
In contrast, inventory management focuses on overseeing goods and materials that are held for sale, production, or consumption. The main objective is to maintain optimal stock levels to meet customer demand without overstocking or running out of stock.
Key aspects of inventory management include:
- Tracking inventory quantities: Ensuring accurate records of available stock.
- Managing reorder points: Determining when to restock items to avoid stockouts.
- Controlling the flow of goods: Ensuring smooth operations and meeting customer needs.
Inventory management also emphasizes supply chain logistics, demand forecasting, and warehouse management. It requires expertise in logistics, procurement, and inventory optimization techniques to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Benefits of asset inventory management
Implementing a robust asset inventory management strategy can yield significant advantages for organizations of any size:
- Cost control and optimization: By avoiding over-purchasing and reducing the likelihood of lost or misused assets, organizations can reinvest cost savings into growth initiatives and innovation.
- Improved operational efficiency: Clear visibility into where assets are located and their current status reduces downtime. This makes maintenance schedules more predictable, and employees spend less time searching for what they need.
- Regulatory compliance and risk management: Many industries face strict regulations regarding the tracking and handling of assets. Additionally, accurate asset records help maintain compliance and reduce the risk of penalties or legal issues.
- Enhanced security and data integrity: Reliable asset data safeguards against theft or unauthorized use, especially for items like laptops, specialized tools, or sensitive digital information.
- Informed decision-making: Comprehensive asset data supports better forecasting, budgeting, and strategic planning. As a result, leaders can determine when to replace or upgrade assets and identify the true costs of ownership over time.
Best practices for effective asset inventory management
To achieve success in asset inventory management, it’s important to follow best practices that blend technology, policies, and human oversight. Here are key strategies to improve efficiency and accuracy:
1. Centralize your asset data
Store all asset information in one place using asset management software or a centralized system. This includes details like purchase dates, current locations, and maintenance history. With everything in one database, you ensure that your records stay up to date, minimizing errors or discrepancies as the status of assets changes. This practice supports lifecycle management, ensuring that asset data is consistent and accessible throughout the asset’s entire lifecycle.
2. Assign unique identification
Make sure every asset is easily identifiable with labels like barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags. Assigning each item a unique ID ensures that anyone in your organization can quickly locate and reference it. This improves tracking and makes it easier to manage maintenance and usage.
3. Conduct regular audits and reconciliations
Set a schedule for regular physical audits, whether quarterly or annually, to check that your asset records match what’s actually in your possession. Using mobile scanners or RFID readers during audits speeds up the process and helps spot any discrepancies, keeping your records accurate and reliable.
4. Implement clear policies and procedures
Create and document standard operating procedures (SOPs) that guide how assets are tracked, moved, and disposed of. Clear policies ensure that everyone in the organization follows the same process, which reduces confusion and errors. Well-established procedures help maintain control over asset handling throughout their entire lifecycle.
5. Ensure adequate staff training
Training your team is key to successful asset management. Regular training should cover how to use your asset management software, input data correctly, and follow SOPs. Designate specific staff, like asset champions or department leads, to help ensure compliance and troubleshoot any issues that arise. A well-trained team tracks and manages assets more efficiently, ensuring smoother operations.
6. Automate and integrate where possible
Use automation tools like IoT sensors and RFID tags to track assets in real time. Set up automatic alerts for maintenance or replacements. Integrate your asset management system with other business tools, such as ERP or finance platforms. This eliminates duplicate data entry and keeps all systems aligned. Together, these steps make asset management more efficient and reliable.
7. Track the full asset lifecycle
Effective asset management means tracking each asset from start to finish, from procurement to disposal. Keep track of depreciation, maintenance schedules, and usage patterns. This helps you plan repairs or replacements at the right time, making sure your assets are always in optimal condition.
8. Focus on security and compliance
For high-value or sensitive assets, implement strong security measures like restricted access or secure storage. Stay updated on industry regulations to ensure your asset management practices remain compliant. Keep thorough, auditable records to make sure you meet all regulatory requirements and are prepared for any audits.
How to Implement Asset Inventory Management
Implementing an effective asset inventory management program involves several key steps. By following this streamlined approach, organizations can ensure accurate tracking, maintenance, and optimal use of their assets.
1. Identify all asset types
Start by creating a catalog of all assets your organization owns. This includes physical items like computers, servers, office furniture, and machinery. Don’t forget software assets like applications, operating systems, and their licenses.
Also, make sure to include virtual machines (VMs), such as virtual servers and their configurations. Cloud-based assets matter too, including cloud storage, SaaS applications, and other online resources.
Categorizing these assets helps organize and manage them effectively, ensuring no asset is overlooked.
2. Choose the right tools
Look for tools that offer automated discovery, which can automatically detect and add new assets to your inventory. This reduces the need for manual entry and minimizes errors.
In addition, real-time tracking features are crucial for continuously monitoring the status and location of assets. Having up-to-date information helps you make quicker, more informed decisions. Finally, make sure the platform integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, enhancing overall efficiency and ensuring data consistency.
3. Assign risk profiles
Evaluating each asset’s importance and potential security risks is an essential step in effective asset inventory management. Begin by assessing the business criticality of each asset, identify which ones are crucial for your operations and which are less vital.
Next, evaluate the security vulnerabilities of each asset by considering the likelihood of threats like cyberattacks or theft. Also, analyze the impact severity, what would happen if an asset were compromised or lost?
Categorizing assets based on these factors allows you to prioritize protection measures and allocate resources more effectively. This ensures that high-risk and high-value assets receive the necessary attention and safeguards.
4. Monitor continuously
Ongoing oversight of your asset inventory is crucial for ensuring both accuracy and security. Use real-time tracking to monitor asset movements and status changes. This allows you to quickly detect unauthorized activities or unusual patterns.
Additionally, set up automated alerts to notify you of events such as unauthorized access attempts or significant changes in asset conditions. Regular updates and synchronization with other systems will help keep your asset data current and accurate.
5. Enforce compliance
Your asset management practices must comply with all relevant regulations and internal policies. This ensures operational integrity and helps you avoid legal penalties.
To make compliance easier, use automated tracking tools. These tools can monitor software licenses, hardware upgrades, and cloud service agreements automatically—reducing the need for manual oversight.
Align your asset management system with industry standards such as GDPR for data protection or HIPAA for healthcare. This ensures that asset handling, data storage, and access controls meet regulatory requirements.
Create clear internal guidelines for asset usage, maintenance, and disposal. These rules help enforce policies consistently. Keep detailed records to simplify audits and prove compliance. Strong enforcement not only prevents legal issues but also strengthens the overall reliability of your asset management practices.
Conclusion
Effective asset inventory management means more than just knowing where your items are. It’s about using resources wisely, cutting costs, and staying compliant.
By following a clear process that includes setting goals, using the right tools, and performing regular audits, organizations can take full control of their assets. This approach helps maximize value throughout each asset’s lifecycle.
Start by reviewing your current asset management practices. Identify key challenges and gaps. Then create a strategy tailored to your organization’s goals. Make sure every resource is tracked, managed, and used to its fullest potential.Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is asset inventory management important?
It helps prevent asset loss, reduce unnecessary purchases, and improve resource allocation. By keeping accurate records of where your assets are and their condition, you can avoid wasting time and money searching for items, reduce the risk of theft, and ensure better decision-making.
2. How do I choose the right asset management system?
Choose a system that automates asset tracking, like using RFID or barcodes, to save time and reduce errors. It should also integrate with your existing tools (like ERP or finance systems) so all your data is in one place. Look for features like real-time updates and the ability to track assets through their entire lifecycle.
3. How can I secure my asset inventory?
Use RFID tags or barcodes to uniquely identify assets, making them easier to track. Set up automated alerts to notify you if an asset moves without authorization. Regularly audit your inventory to spot discrepancies and ensure high-value items are stored in secure locations with restricted access.