What is Cloud Asset Management in ITAM? Key Features and Functions
Cloud Asset Management helps businesses track, secure, and reduce costs on cloud resources. Learn how to manage assets efficiently and improve IT operations.
Cloud systems give businesses the tools to grow and adjust easily. Teams can add or change resources quickly as their needs change.
But this flexibility also creates challenges. Cloud assets can grow fast and become hard to track. When that happens, teams lose visibility, spend too much on unused resources, and face security risks.
Cloud asset management helps fix these problems. It keeps track of all assets, controls costs, and keeps systems safe and compliant.
What Are Cloud Assets?
Cloud assets are IT resources that live in the cloud. They can include servers, storage, software, or data used online. Unlike equipment kept in an office, these assets are not physical and can change often. This makes them harder to track with normal inventory tools.
To stay in control, organizations need tools made for cloud management. These tools help keep visibility, protect data, and manage costs more effectively.
Here are some key types of cloud assets and what makes them unique:
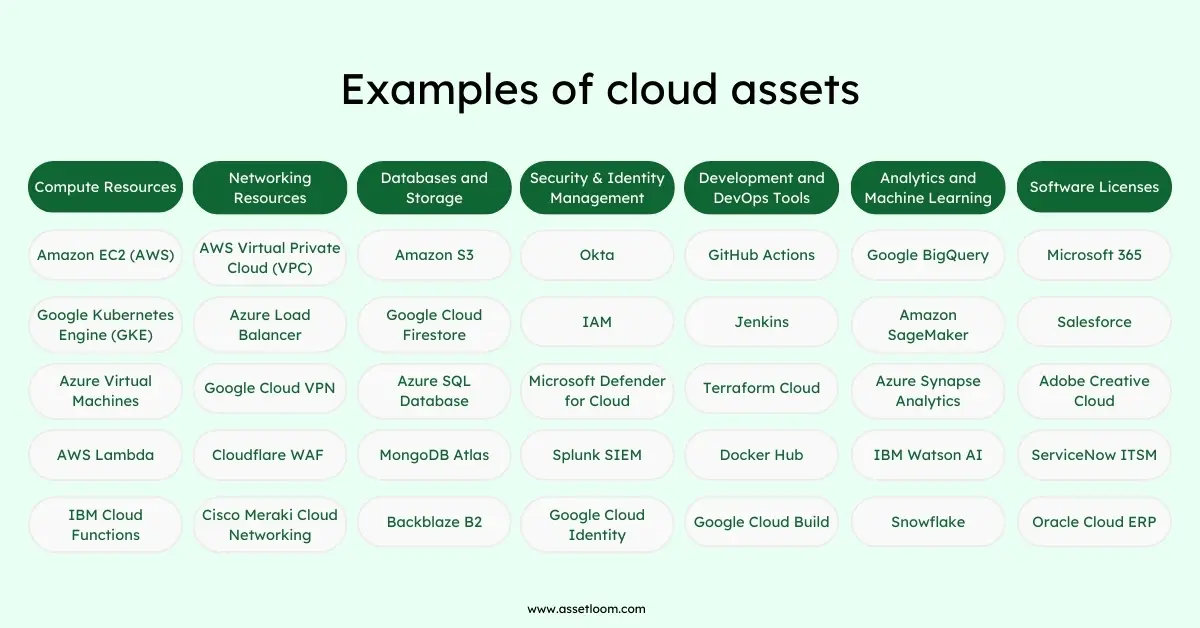
Compute Resources
Cloud compute resources support workloads and applications. These include virtual machines (VMs) , containers, and serverless computing services, along with the physical infrastructure they run on.
Many businesses use platforms such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Others choose private or hybrid setups that mix both.
To manage these assets well, teams need to know what they use, how it’s configured, and how much it costs. Tracking these details helps avoid waste and keeps systems running smoothly.
Networking Resources
Networking resources connect cloud systems and keep data moving safely. They include virtual routers, firewalls, load balancers, and network management tools.
These tools work completely in the cloud instead of using physical devices. This makes networks easier to grow and adjust when needed.
However, cloud networks can become complex quickly. Teams need strong asset management to track settings, watch performance, and keep security in check.
Databases and Storage
Cloud databases and storage systems replace traditional in-office servers. They provide flexible space that grows or shrinks based on demand.
These resources include relational databases, NoSQL databases, data lakes, and backup storage. They store large amounts of business data safely and make it easy to access from anywhere.
Because they hold important information, teams need to track how these assets are used. Good tracking helps improve performance, control access, and reduce security risks.
Security and Identity Management
Cloud security tools help protect systems and control access. They detect threats and keep data safe across cloud platforms.
These tools include XDR platforms, authentication services, and SIEM tools for tracking security events.
Managing them well makes sure security rules are followed and compliance standards are met. This helps keep cloud environments safe and trusted.
Development and DevOps Tools
Software development and DevOps tools power cloud application lifecycles. CI/CD pipelines, container orchestration tools, and collaboration platforms are cloud assets that need to be tracked like any other resource. Managing these tools ensures efficient software deployment, compliance with licensing agreements, and cost control.
Analytics and Machine Learning
Cloud-based analytics and AI tools process vast amounts of data for business insights. These assets include big data processing tools, machine learning models, and cloud dashboards. Organizations must manage them to control access, secure sensitive data, and ensure cost-effective usage.
Software Licenses
Both in-house and third-party software require proper licensing, especially in multi-cloud and hybrid environments. Managing software licenses as cloud assets prevents compliance issues, overspending, and version control problems. Cloud asset management solutions provide a centralized view of license usage, renewals, and expiration dates.
What is cloud asset management?
Cloud Asset Management (CAM) is the process of tracking and managing all resources in the cloud. It helps keep assets organized, secure, and cost-effective.
Traditional tracking methods, like spreadsheets, are not enough. Cloud resources can be created or removed in seconds, making manual tracking slow and inaccurate.
Why It Matters
Without a proper system, teams can face:
- Lost visibility – not knowing what resources exist or who uses them.
- Higher costs – paying for unused or forgotten assets.
- Security risks – unmonitored assets can create weak points.
How CAM Helps
Cloud Asset Management solves these issues by using automated tools that:
- Track cloud assets in real time.
- Categorize resources by usage, cost, or type.
- Help teams control access and stay compliant with policies.
With CAM, organizations can scale their cloud use safely while keeping full control of their digital resources.
Advantages of Cloud Asset Management
Cloud Asset Management (CAM) helps businesses manage both physical and virtual assets in the cloud. It improves visibility, automation, security, and cost control, making cloud operations smoother and more efficient.
Key Advantages
1. Better Visibility CAM gives a clear view of all cloud assets in one place.
- Tracks every resource automatically.
- Reduces the chance of missing or duplicate assets.
- Helps teams use resources effectively and prevent disruptions.
2. Automation and Efficiency CAM automates asset discovery, tracking, and cost monitoring.
- Cuts down manual work.
- Updates assets in real time.
- Keeps systems accurate as the cloud environment grows.
3. Stronger Security and Compliance CAM helps apply security rules and detect weaknesses early.
- Monitors user access and system changes.
- Supports compliance with industry standards.
- Reduces security risks through early alerts and audits.
4. Cost Control and Savings CAM helps lower costs by showing how assets are used.
- Identifies unused or idle resources.
- Reduces maintenance and licensing expenses.
- Supports preventive actions to avoid costly failures.
Features & Functions of Cloud Asset Management in ITAM
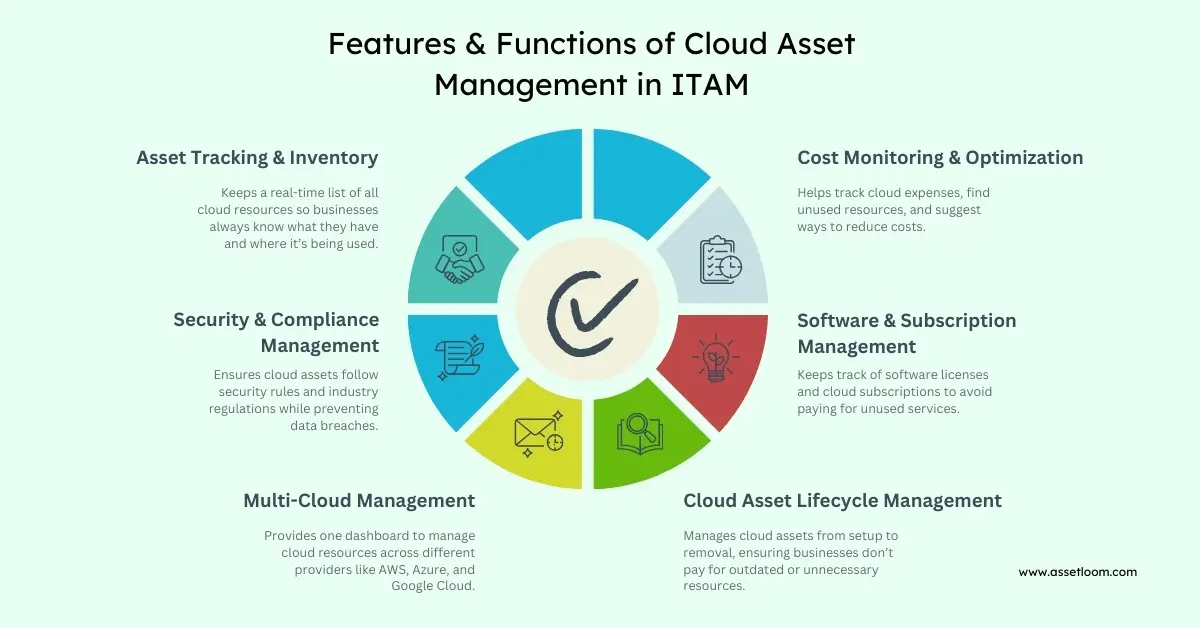
1. Asset Discovery & Inventory Management
Cloud environments change all the time. New resources are created, and old ones are removed or forgotten. Without proper tracking, it’s easy for businesses to lose sight of what they own.
Cloud Asset Management helps by finding and listing all cloud resources in real time. It keeps everything—like virtual machines, databases, and storage—visible in one place.
For example, a company using AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud can automatically detect all active assets across these platforms. This helps teams avoid waste, reduce security risks, and always know what resources they have and how they’re used.
2. Cost Tracking & Optimization
Cloud services can get expensive fast. Many companies pay for resources they don’t use or need.
Cloud Asset Management tracks spending as it happens. It shows which resources cost the most and which ones are sitting idle.
For example, if virtual machines run all night but are only needed during the day, the system can suggest turning them off after work hours.
This helps businesses save money, use resources wisely, and keep cloud costs under control.
3. Compliance & Security Management
Security and compliance are major concerns in the cloud. Small mistakes, like wrong settings or weak access rules, can expose data and cause breaches.
Cloud Asset Management helps keep systems safe. It applies security rules, checks for weak spots, and tracks compliance with standards such as GDPR and ISO.
For example, if a company stores sensitive data in the cloud, the system can find any unprotected storage and alert the IT team right away.
By keeping assets secure and compliant, businesses can avoid fines, protect data, and build trust with their customers.
4. License & Subscription Management
Tracking cloud software and subscriptions can be tricky. Many companies pay for licenses they don’t use or let renewals happen automatically.
Cloud Asset Management gives a clear view of all software licenses, renewals, and active users. It helps teams see what is used and what is not.
For example, if a company pays for 500 Microsoft 365 accounts but only 400 are active, the system can flag the extra licenses and suggest changes.
This helps businesses save money, avoid waste, and stay compliant with software rules.
5. Hybrid & Multi-Cloud Management
Many companies use more than one cloud provider. This often leads to scattered resources, different rules, and wasted spending.
Cloud Asset Management brings everything together in one dashboard. It helps teams manage assets across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and private cloud systems.
For example, if a company runs apps on both AWS and Azure, the system can compare performance and costs. IT teams can then choose where to run each app for better efficiency.
This makes cloud management simpler and helps businesses get more value from their cloud investments.
6. Asset Lifecycle Management
Cloud assets go through different stages — setup, use, upgrades, and retirement. Without proper tracking, some resources stay active long after they’re needed. This can waste money and increase security risks.
Cloud Asset Management automates each stage of the asset lifecycle. It helps teams use resources efficiently and remove them when they’re no longer needed.
For example, a company using cloud-based virtual desktops can set an auto-delete rule for inactive accounts after a certain time. This stops unnecessary costs and keeps the cloud system clean and secure.
Managing the full lifecycle keeps cloud assets organized, cost-effective, and safe.
Take control of your cloud assets with AssetLoom. Track, secure, and optimize your IT resources effortlessly. Start managing smarter today!
Onboarding Cloud Assets Into the IT Environment
Bringing cloud assets into an IT environment requires a structured approach to keep everything organized, secure, and cost-efficient. Without proper onboarding, businesses risk losing track of assets, overspending, and exposing data to security threats. A well-planned process ensures cloud resources are properly integrated and managed from the start.
1. Categorizing Cloud Assets
Cloud environments contain many types of assets, including compute resources (virtual machines, containers), storage, networking tools, security applications, and SaaS software. Categorizing them helps businesses track usage, allocate resources efficiently, and avoid duplication. Clear classification also makes it easier to monitor costs and ensure compliance with internal policies.
2. Automating Asset Discovery and Tagging
Cloud resources are constantly being created and updated, making manual tracking nearly impossible. Automated discovery tools can detect new assets in real time, ensuring all resources are accounted for. Using automated tagging, businesses can label assets by department, project, or owner, making it easier to manage and monitor them. This prevents uncontrolled cloud growth (cloud sprawl) and helps maintain clear oversight of all assets.
3. Integrating with IT Asset Management (ITAM) Systems
To maintain control, cloud assets should be tracked alongside traditional IT assets. Integrating cloud resources into an IT Asset Management (ITAM) system provides a single source of truth for all assets. This allows businesses to monitor usage, track costs, manage lifecycles, and ensure compliance more efficiently. ITAM integration also improves audits by keeping detailed records of all cloud resources.
4. Implementing Security and Access Controls
Security must be a top priority when onboarding cloud assets. Without proper controls, unauthorized access and misconfigurations can lead to data breaches. Organizations should implement:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Restricts asset access based on user roles.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adds an extra layer of security to cloud accounts.
- Encryption Policies – Protects data from unauthorized access.
- Automated Compliance Checks – Ensures assets meet security regulations like GDPR and ISO.
These measures help businesses protect sensitive data and reduce cybersecurity risks.
5. Setting Up Cost Management and Budgeting
Cloud costs can add up quickly if not properly monitored. Setting budget limits and tracking usage ensures businesses only pay for what they need. Best practices for cost control include:
- Monitoring real-time spending to prevent unexpected costs.
- Setting budget alerts to notify teams when spending exceeds limits.
- Using auto-scaling to match resource demand.
- Optimizing workloads by shutting down unused resources.
With the right cost management strategy, businesses can reduce waste and make cloud spending more predictable.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Once cloud assets are onboarded, ongoing monitoring ensures they remain efficient, secure, and cost-effective. Businesses should:
- Review performance regularly to optimize resource usage.
- Use AI-driven insights to predict future cloud needs.
- Conduct security audits to detect vulnerabilities.
- Decommission unused resources automatically to reduce costs.
Continuous optimization ensures cloud assets stay aligned with business goals and provide maximum value.
Best practices for cloud asset management
Effective cloud asset management ensures visibility, security, and cost efficiency in an organization’s IT environment. Following best practices helps businesses optimize cloud resources, prevent waste, and maintain compliance.
1. Maintain a Centralized Asset Inventory
Keep all cloud assets in a single, centralized inventory for full visibility. Regularly update it to track active, unused, and decommissioned resources across all cloud providers.
2. Automate Asset Discovery and Tracking
Use automated tools to detect, tag, and monitor cloud assets in real time. This prevents shadow IT, reduces manual errors, and ensures accurate tracking of all resources.
3. Implement Strong Security Controls
Apply role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect assets. Regularly audit security settings to detect vulnerabilities and prevent unauthorized access.
4. Optimize Cloud Costs
Monitor spending with cost-tracking tools, budget alerts, and usage reports. Identify idle or oversized resources and eliminate waste through rightsizing and auto-scaling.
5. Ensure Compliance and Governance
Enforce regulatory compliance (GDPR, ISO, NIST) by maintaining audit logs, tracking license agreements, and implementing standardized cloud policies.
6. Streamline Asset Lifecycle Management
Manage assets from procurement to decommissioning to avoid unnecessary renewals and outdated resources. Automate provisioning, updates, and retirement to keep cloud environments optimized.
7. Integrate with IT Service Management (ITSM)
Connect cloud asset management with ITSM tools to improve incident tracking, change management, and automated workflows for better IT operations.
Conclusion
Cloud asset management is key to keeping visibility, security, and cost control in modern IT systems. Without it, businesses can face high costs, security gaps, and compliance problems.
By using automated tracking, cost control, and strong security rules, teams can manage assets better. Lifecycle management also helps reduce waste and improve daily operations.
A clear and structured approach ensures every resource is used wisely and kept secure. As cloud use continues to grow, companies that follow best practices and use automation will manage their IT assets more effectively and stay ahead.